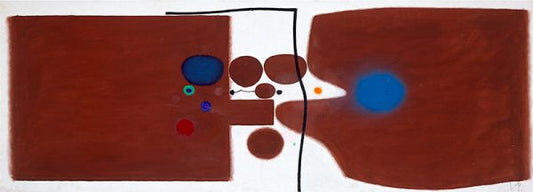
Collection: Victor Passmore
Limited edition giclee prints after Victor Pasmore.
Pasmore represented Britain at the 1961 Venice Biennale, was a participating artist at the Documenta II 1959 in Kassel and was a trustee of the Tate Gallery, donating a number of works to the collection. He gave a lecture on J.M.W. Turner as 'first of the moderns' to the Turner Society, of which he was elected a vice president in 1975.
Pasmore's break into abstract art was inspired by the artists Piet Mondrian and Paul Klee. Their writings feature nature and the creation of a dynamic harmony in art which stood for the future harmony of society.

Collapsible content
More on Victor Passmore
Victor Pasmore was born in Chelsham, Surrey, on 3 December 1908.[He studied at Summer Fields School in Oxford and Harrow in west London, but with the death of his father in 1927 he was forced to take an administrative job at the London County Council. He studied painting part-time at the Central School of Art and was associated with the formation of the Euston Road School. After experimenting with abstraction, Pasmore worked for a time in a lyrical figurative style, painting views of the River Thames from Hammersmith much in the style of Turner and Whistler.
In the Second World War, Pasmore was a conscientious objector. Having been refused recognition by his Local Tribunal, he was called up for military service in 1942. He refused orders and was court martialled and sentenced to 123 days imprisonment. The sentence qualified him to go to the Appellate Tribunal in Edinburgh, which allowed him unconditional exemption from military service.
Pasmore's break into abstract art was inspired by the artists Piet Mondrian and Paul Klee. Their writings feature nature and the creation of a dynamic harmony in art which stood for the future harmony of society.
Beginning in 1947, he developed a purely abstract style under the influence of Ben Nicholson and other artists associated with Circle, becoming a pioneering figure of the revival of interest in Constructivism in Britain following the War.[ Pasmore's abstract work, often in collage and construction of reliefs, pioneered the use of new materials and was sometimes on a large architectural scale. Herbert Read described Pasmore's new style as "The most revolutionary event in post-war British art".
In 1950, he was commissioned to design an abstract mural for a bus depot in Kingston upon Thames[ and the following year Pasmore contributed a mural to the Festival of Britain that promoted a number of the British Constructivists.
Pasmore was a supporter of fellow artist Richard Hamilton, giving him a teaching job in Newcastle and contributing a constructivist structure to the exhibition "This Is Tomorrow" in collaboration with Erno Goldfinger and Helen Phillips. Pasmore was commissioned to make a mural for the new Newcastle Civic Centre. His interest in the synthesis of art and architecture was given free hand when he was appointed Consulting Director of Architectural Design for Peterlee development corporation in 1955. Pasmore's choices in this area proved controversial; the centerpiece of the town design became an abstract public art structure of his design, the Apollo Pavilion. The structure became the focus for local criticism over the failures of the Development Corporation but Pasmore remained a defender of his work, returning to the town to face critics of the Pavilion at a public meeting in 1982. After many years of neglect the work was restored in 2009 with a grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund.[
Pasmore represented Britain at the 1961 Venice Biennale, was participating artist at the Documenta II 1959 in Kassel and was a trustee of the Tate Gallery, donating a number of works to the collection. He gave a lecture on J.M.W. Turner as 'first of the moderns' to the Turner Society, of which he was elected a vice president in 1975.
-
Victor Pasmore - A Tree Full of Birds
Regular price From £148.00 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per -
Victor Pasmore - Brown Symphony
Regular price From £148.00 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per -
Victor Pasmore - Points of Contact No.24
Regular price From £175.00 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per -
Victor Pasmore - The Abstract
Regular price From £175.00 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per